10 Tips and Tricks for SharePoint Online Administration
SharePoint Online, a cornerstone of modern enterprise collaboration and content management, offers administrators a range of tools and features to optimize and secure their digital workspace. This article delves into several advanced tips and techniques, offering in-depth insights for SharePoint Online administrators to elevate their site management and user engagement strategies.
Key Takeaways:
| Tip | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Robust Permission Structure | Implement layered permissions aligned with organizational roles for enhanced security. |
| SharePoint Groups | Use groups for streamlined user management and consistent access control. |
| Hub Sites | Centralize and connect related sites for unified navigation and shared resources. |
| Content Types & Metadata | Utilize content types and metadata for efficient data organization and retrieval. |
| SharePoint Workflows | Automate business processes to improve efficiency and consistency. |
| Site Policies | Manage site lifecycles effectively through governance policies. |
| Customizing SharePoint Search | Enhance search functionality for more accurate and user-friendly results. |
| Monitoring SharePoint Health & Usage | Use analytics for insights into site performance and user engagement. |
| Managing SharePoint Storage | Implement storage quotas and monitor usage to maintain optimal system performance. |
| Staying Updated with SharePoint Online | Regularly update and test new features to leverage advancements and maintain security. |
Tip 1: Implementing a Robust Permission Structure
Overview: Permissions in SharePoint Online are the backbone of security and content management. A well-structured permission system ensures sensitive information is adequately protected while making necessary content accessible to the right users.
How-To: Start by creating a comprehensive map of your organizational structure and content hierarchy. Define roles and responsibilities clearly and align them with SharePoint’s permission levels. It’s essential to understand the difference between SharePoint groups, permission levels, and inheritance.
- Site Collection Permissions: At the top level, manage who has full control, owner, and visitor access. Be cautious with ‘Full Control’ permissions, as they allow users to make significant changes.
- Subsite and Library Permissions: Break inheritance judiciously to give specific access to subsites, libraries, and lists. Use groups to assign permissions to these entities, ensuring a clear and manageable permission structure.
- Item-Level Permissions: For highly sensitive documents, use item-level permissions to restrict access. While powerful, be aware this can become complex to manage.
Technical Insight: Use PowerShell scripting to handle complex permission setups or bulk changes. Understand SharePoint’s security trimming feature, which automatically hides content from users who don’t have the appropriate permissions. Regularly audit your permissions setup to ensure it aligns with current organizational needs and compliance requirements.
Challenges and Considerations: Avoid over-complicating the structure. Too many layers can lead to management difficulties and user confusion. Strive for a balance between security and usability.

Tip 2: Leveraging SharePoint Groups for Efficient User Management
Overview: SharePoint groups are a fundamental aspect of managing user access. They simplify the assignment of permissions and ensure consistent access control across your SharePoint environment.
How-To: Create groups that reflect your organization’s departments or teams. For instance, a ‘Marketing Team’ group can have access to specific marketing project sites and libraries.
- Creating and Managing Groups: Use the SharePoint admin center to create new groups. Assign a set of permissions to each group based on their role.
- Adding and Removing Users: Regularly update group memberships to reflect changes in your team. Automate this process by integrating with Azure AD, where possible, to sync group memberships based on organizational roles.
Technical Insight: Utilize group settings to define who can view and edit group membership. Consider creating ‘Audience’ groups for targeted content delivery. Use Microsoft 365 groups for a more integrated experience across various Microsoft applications.
Challenges and Considerations: Regular maintenance of group memberships is crucial to prevent ‘orphaned’ users or groups. Monitor the groups for relevancy and update them as your organization evolves.
Mastering SharePoint Online
Please fill out the form below to get our free Ebook "Mastering SharePoint Online" emailed to you
Send download link to:
Tip 3: Utilizing SharePoint Hub Sites
Overview: Hub sites in SharePoint Online offer a way to connect and organize sites based on project, department, or region, providing a common navigational structure and shared resources.
How-To: Identify the key areas of your organization that could benefit from a connected approach. Convert an existing site to a hub site through the SharePoint admin center or create a new one.
- Setting Up a Hub Site: In the SharePoint admin center, select the site you wish to convert into a hub site. Use the ‘Register as hub site’ option and configure its settings, including name and description.
- Connecting Sites to the Hub: Choose related sites to associate with this hub. This connection allows for centralized navigation, shared themes, and content roll-up across associated sites.
Technical Insight: Utilize the SharePoint Online Management Shell for bulk operations on hub sites. You can script the connection and disconnection of multiple sites to a hub site. Take advantage of hub site search scope for unified search results across all associated sites.
Challenges and Considerations: Avoid creating too many hub sites, which can lead to a disjointed user experience. Strategically plan hub sites to mirror your organization’s structure and workflow.

Tip 4: Advanced Data Management with Content Types and Metadata
Overview: Content types and metadata in SharePoint Online provide a powerful way to organize, manage, and retrieve content efficiently.
How-To: Establish a standardized set of content types and metadata for your organization.
- Defining Content Types: Create content types that represent different kinds of documents and items in your organization, such as ‘Project Plans’ or ‘Expense Reports’. Include specific metadata fields in each content type for detailed categorization.
- Implementing Metadata: Utilize metadata fields to tag and categorize documents. This approach allows for dynamic views in libraries and more effective search results.
Technical Insight: Leverage the Content Type Hub for organization-wide content type publishing. Use Managed Metadata Service to create a centralized term store for consistent taxonomy across your SharePoint environment.
Challenges and Considerations: Regularly review and update your content types and metadata to ensure they stay relevant and useful. Train users on the importance and usage of metadata for improved compliance and retrieval efficiency.
SharePoint Storage Explorer
Gain insights in to your SharePoint Online Storage Consumption
Download our completely FREE TOOL
Send download link to:
Tip 5: Automating Processes with SharePoint Workflows
Overview: SharePoint workflows are essential for automating repetitive tasks, improving efficiency, and ensuring process consistency across the organization.
How-To: Identify common processes in your organization that can benefit from automation. Use SharePoint Designer or Power Automate to create workflows.
- Creating Workflows: In SharePoint Designer, choose the type of workflow (List, Reusable, or Site) and define the conditions and actions. For more complex workflows, consider using Power Automate, which offers integration with a wider range of services and advanced logic capabilities.
- Deploying and Managing Workflows: Test workflows in a controlled environment before deployment. Monitor their performance and make adjustments as necessary.
Technical Insight: Utilize workflow history logs to troubleshoot issues. In Power Automate, leverage advanced expressions and custom connectors for sophisticated automation scenarios.
Challenges and Considerations: Keep workflows as simple as possible to ensure they are maintainable and scalable. Regularly update and review workflows to align with changing business processes.

Tip 6: Implementing SharePoint Site Policies
Overview: Site policies in SharePoint Online help manage the lifecycle of sites, ensuring they remain relevant and compliant.
How-To: Develop site policies that reflect your organization’s data governance and compliance requirements.
- Creating Site Policies: In the SharePoint admin center, define site closure and deletion policies. Set up rules for archiving sites and content, specifying retention periods and actions to be taken when a site becomes inactive.
- Applying Site Policies: Associate these policies with sites during their creation or through site settings. Ensure that site owners are aware of the policies and their implications.
Technical Insight: Use PowerShell scripts to apply site policies across multiple sites efficiently. Monitor compliance with these policies through SharePoint’s reporting tools.
Challenges and Considerations: Balancing between too rigid and too lax policies is crucial. Regularly review and update site policies to adapt to organizational changes or regulatory requirements.
Tip 7: Customizing SharePoint Search for Optimal Results
Overview: Tailoring the SharePoint Online search experience is crucial for helping users find relevant information quickly and efficiently.
How-To: Enhance your SharePoint search functionality by customizing search schemas and managed properties.
- Configuring Search Schemas: Modify the search schema to include custom managed properties that align with your organization’s content. This allows for more precise search results based on specific content types or metadata.
- Improving Search Experience: Implement search refiners and customize search result pages to provide a more intuitive and user-friendly search experience. Utilize query rules to promote or demote search results based on certain conditions.
Technical Insight: Leverage SharePoint PnP PowerShell to automate search configuration across your environment. Consider integrating Microsoft Search for a more cohesive search experience across Microsoft 365.
Challenges and Considerations: Balancing between over-customization and under-utilization of search features. Regularly gather user feedback to refine the search experience.

Tip 8: Monitoring SharePoint Online Health and Usage
Overview: Regular monitoring of SharePoint Online’s health and usage is key to maintaining a high-performing and efficient environment.
How-To: Utilize SharePoint’s built-in analytics tools to gain insights into site usage, user activity, and system health.
- Using SharePoint Analytics: Access usage reports in the SharePoint admin center to track how users are interacting with sites. Monitor trends in page views, search queries, and document downloads.
- System Health Monitoring: Keep an eye on service health dashboards and set up alerts for any issues or outages in SharePoint Online.
Technical Insight: Advanced administrators can use Microsoft Graph API to create custom reports or integrate with third-party monitoring tools for more detailed analytics.
Challenges and Considerations: Data interpretation and action. Use analytics insights to make informed decisions about training, content management, and system optimizations.
Tip 9: Managing SharePoint Online Storage
Overview: Effective management of storage in SharePoint Online is essential to ensure optimal performance and avoid unnecessary costs.
How-To: Regularly review and manage storage allocation across your SharePoint environment.
- Monitoring Storage Usage: Use the SharePoint admin center to monitor storage usage across site collections. Keep an eye on large sites and libraries that may consume disproportionate amounts of storage.
- Implementing Storage Quotas: Set storage limits for site collections to prevent unchecked growth. Educate site owners about managing their storage usage effectively.
- Use SharePoint Storage Explorer: To see how much SharePoint Online Storage you are using, per SharePoint Site or Document Library. Dont forget this tool is FREE.
Technical Insight: Utilize PowerShell scripts to automate storage reports and enforce quotas across multiple site collections. Consider leveraging cloud storage solutions for large or infrequently accessed files.
Challenges and Considerations: Balancing storage needs with cost. Regularly review storage policies to ensure they align with current organizational needs and budget constraints.

Tip 10: Staying Up-to-Date with SharePoint Online Updates
Overview: Keeping abreast of the latest updates in SharePoint Online is crucial for leveraging new features and maintaining security.
How-To: Regularly check Microsoft’s release notes and updates for SharePoint Online.
- Following Release Cycles: Familiarize yourself with Microsoft’s release cycle for SharePoint Online, which includes targeted release (for early access) and standard release.
- Testing New Features: Create a test environment to evaluate new features and updates before rolling them out organization-wide. This helps in identifying any potential issues or training needs.
Technical Insight: Participate in SharePoint community forums and follow SharePoint-focused blogs for insights and best practices. Use the Microsoft 365 admin center to manage update settings and preferences.
Challenges and Considerations: Balancing the adoption of new features with stability and user training. Ensure that updates align with your organization’s IT strategy and user readiness.
Tip 11: Leverage Squirrel for Optimized Document Archiving and Cost Reduction
Streamline Your SharePoint Storage with Squirrel: Managing the sheer volume of documents in SharePoint Online can be challenging and costly. Squirrel offers a robust solution by automating the archiving of older, less frequently accessed documents to Azure Blob Storage, thus optimizing your SharePoint storage. This helps maintain a leaner, more efficient SharePoint environment.
How to Implement Squirrel:
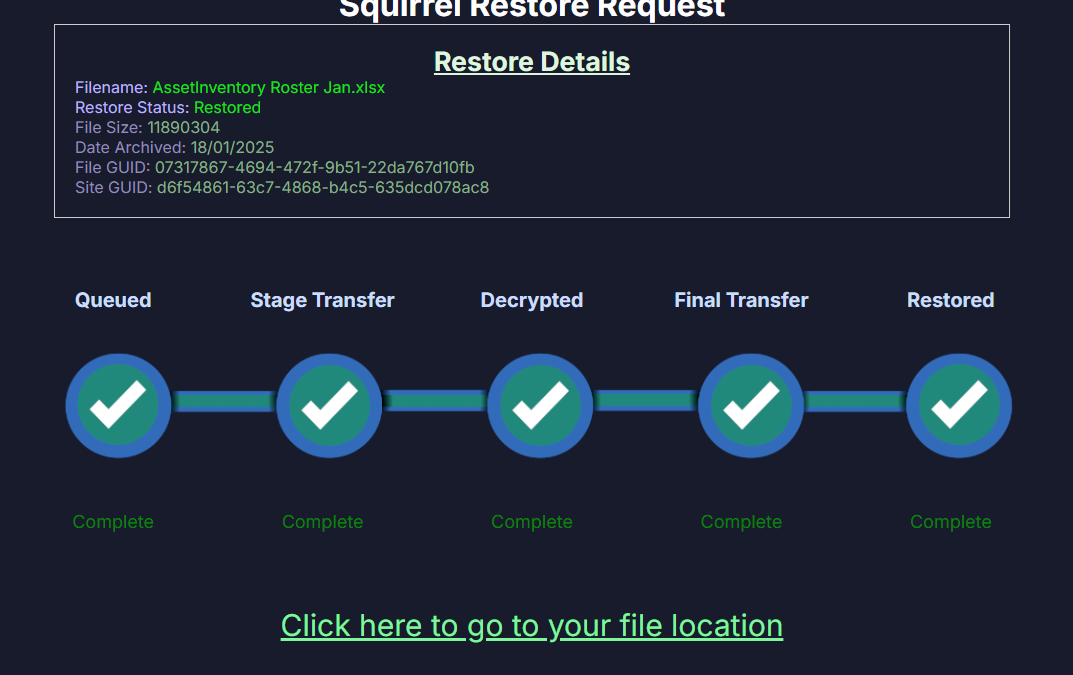
- Identify Eligible Documents: Start by determining which documents are accessed infrequently. Squirrel can be configured to automatically move these documents based on predefined criteria such as age or last accessed date.
- Set Archiving Rules: Define your archiving rules within Squirrel to match your organizational needs. You can customize rules based on document type, project, or department, ensuring that only relevant documents remain active in your primary SharePoint sites.
- Monitor and Adjust: Use the Squirrel dashboard to monitor the archiving process and the impact on your SharePoint performance. Make adjustments to archiving rules as necessary to continually optimize the balance between accessibility and cost efficiency.
Benefits of Using Squirrel:
- Reduced Costs: By archiving documents to Azure Blob Storage, you can significantly reduce the costs associated with SharePoint storage, particularly if you are nearing your storage limit and facing the prospect of purchasing additional capacity.
- Enhanced Performance: With fewer documents cluttering your SharePoint environment, you’ll experience faster search results and quicker load times, enhancing user satisfaction.
- Compliance and Security: Squirrel ensures that all archived documents are handled securely and in compliance with regulatory requirements, using encryption in transit and at rest.
Integrating Squirrel into your SharePoint strategy not only improves operational efficiency but also cuts costs and enhances document management across your organization. As part of your SharePoint maintenance routine, consider how Squirrel can make your document storage more dynamic and cost-effective.
FAQs
- How can I ensure optimal security with SharePoint Online permissions?
- Implement layered permissions aligned with organizational roles, regularly review and update permissions, and utilize item-level permissions for sensitive documents.
- What are the best practices for managing user roles with SharePoint groups?
- Create groups reflecting organizational departments or teams, assign consistent permissions to these groups, and integrate with Microsoft 365 groups for enhanced functionality.
- How do Hub Sites enhance site organization in SharePoint Online?
- Hub Sites centralize and connect related sites, providing unified navigation, shared resources, and consistent branding across associated sites.
- What are the advantages of using content types and metadata in SharePoint?
- They enable efficient data organization and retrieval, allowing for dynamic views in libraries and more effective search results through standardized document categorization.
- How can SharePoint workflows be used to automate business processes?
- Use SharePoint Designer or Power Automate to create workflows that automate tasks like document approvals, data collection, and routine administrative processes.
- What should be considered when implementing site policies in SharePoint Online?
- Develop policies that reflect data governance and compliance requirements, set up rules for archiving, and apply policies to manage site lifecycles effectively.
- How can I customize SharePoint search for better user experience?
- Modify the search schema to include custom managed properties, implement search refiners, and customize search result pages for precise and user-friendly search experiences.
- What are effective ways to monitor SharePoint Online health and usage?
- Use SharePoint’s built-in analytics tools to track site usage and user activity, and monitor system health through service health dashboards and alerts.
- How do I manage SharePoint Online storage efficiently?
- Monitor storage usage regularly, set storage quotas for site collections, and consider integrating cloud storage solutions for large files.
- Why is it important to stay updated with SharePoint Online, and how can I do it?
- Staying updated ensures you leverage new features and maintain security. Regularly check Microsoft’s release notes, test new features in a controlled environment, and follow SharePoint community forums for updates.