SharePoint Terminology Guide
App:
An app in SharePoint is a small, purpose-specific application or program that adds new features or functionality to a SharePoint site. These apps can be installed from the SharePoint Store or developed specifically for your needs. They help to customize the SharePoint experience without complex coding.
Example: An app that provides a calendar for booking meeting rooms. Team members can check room availability and reserve rooms directly from the SharePoint site.
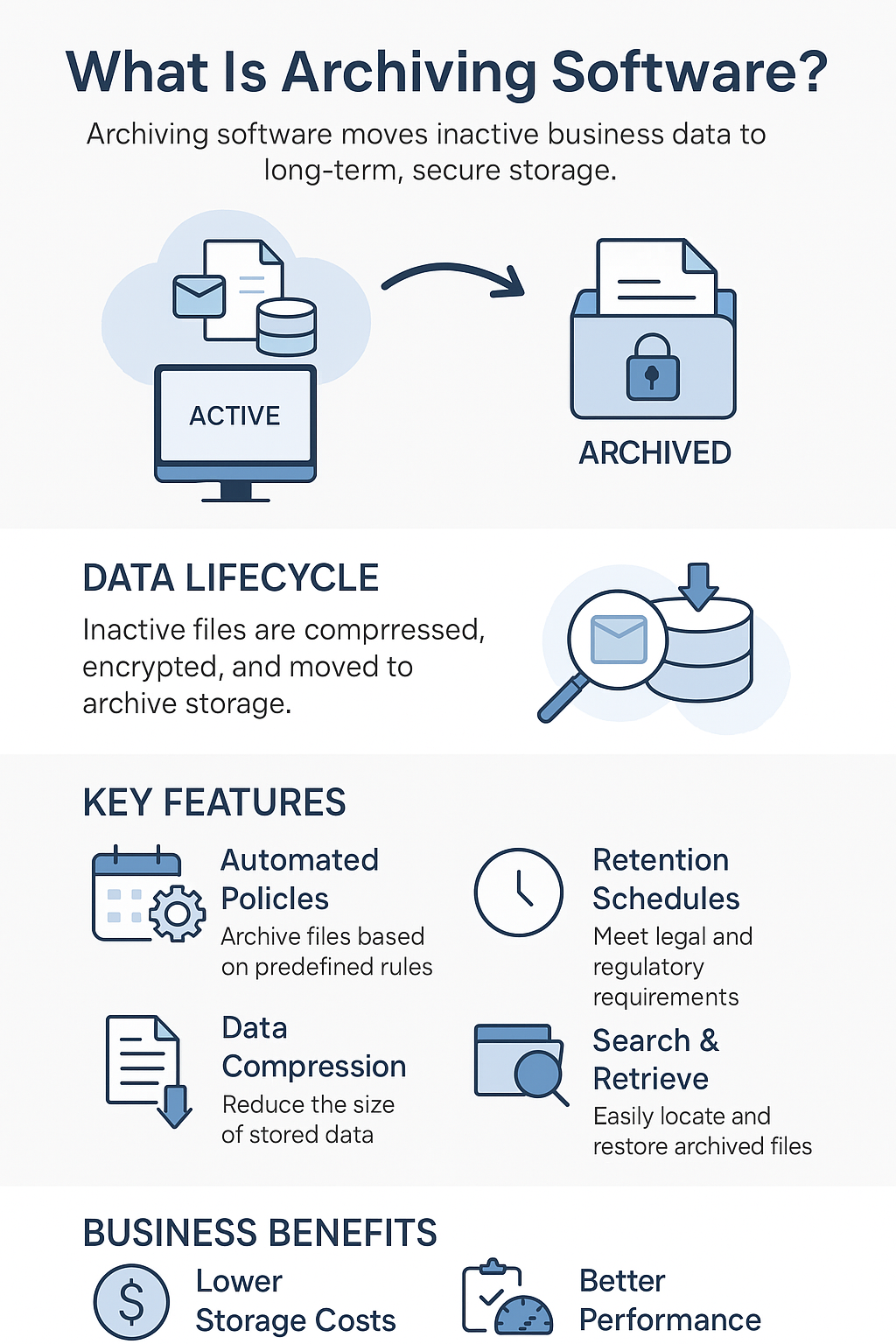
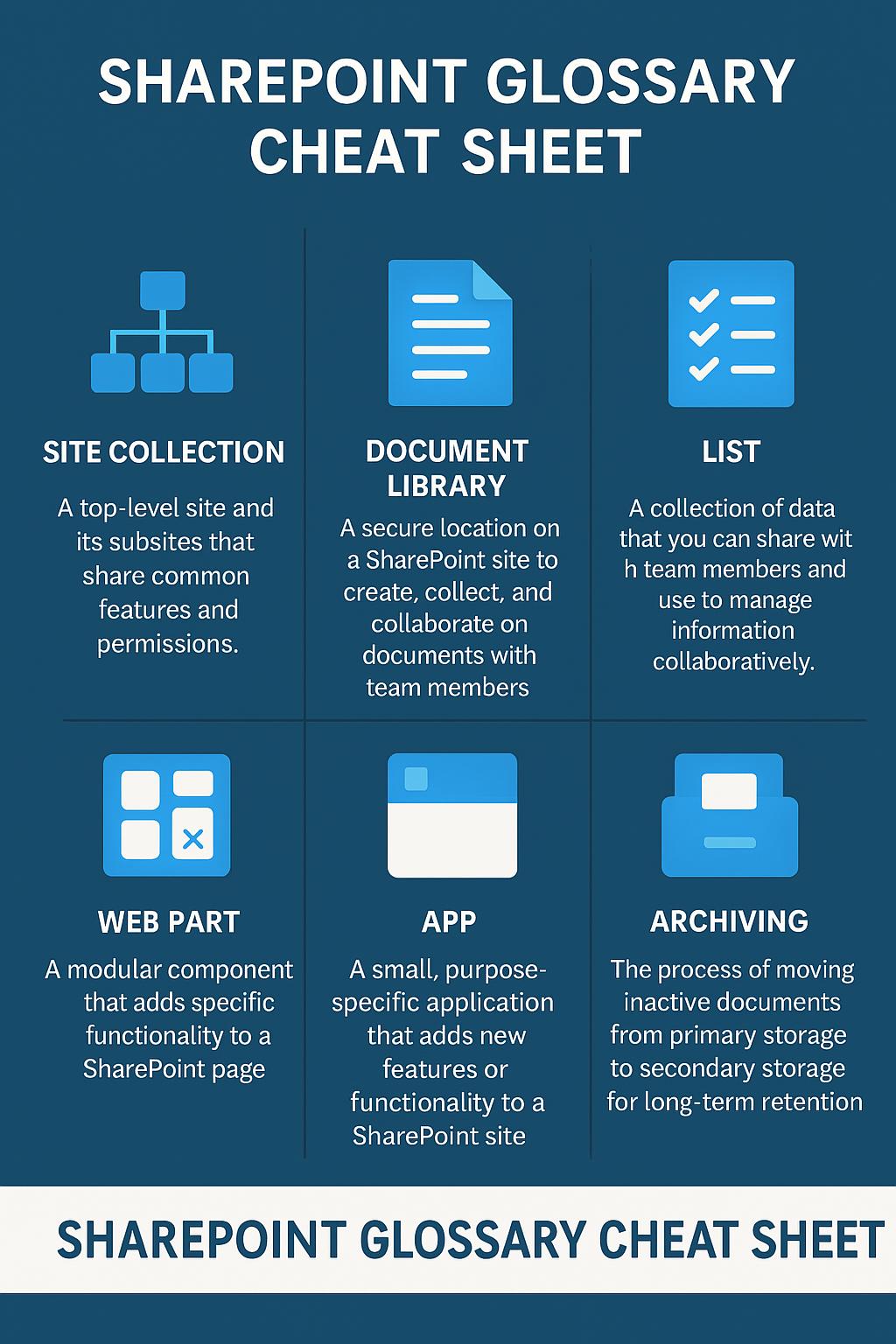
Archiving:
Archiving in SharePoint refers to moving inactive documents from primary storage to secondary storage for long-term retention, freeing up space and improving system performance.
Example: A company uses SharePoint to manage project files. Older documents that haven’t been accessed in over a year are automatically moved to Azure Blob Storage. This reduces storage costs and maintains easy access to archived documents via stub files left in SharePoint.
BCS (Business Connectivity Services):
BCS stands for Business Connectivity Services. It allows SharePoint to connect and interact with external data sources, such as databases or web services, making it possible to display and manipulate external data as if it were native to SharePoint. This integration helps consolidate different data sources into a single interface.
Example: Integrating an external SQL Server database that stores customer information into SharePoint, so employees can view and update customer data directly from a SharePoint list.
Check-in/Check-out:
Check-in and check-out are features that help manage document editing by multiple users. When a document is checked out, it is locked for editing by one person, preventing others from making changes simultaneously. Once the editing is complete, the document is checked back in, making the updated version available to others.
Example: Alice checks out a financial report to update quarterly figures. During this time, Bob and Carol can see the report but cannot edit it. When Alice finishes her updates, she checks the report back in, allowing Bob and Carol to make further changes if needed.
Column:
A column in SharePoint is a vertical section in a list or library that holds a specific type of information. Columns help organize and categorize data, making it easier to manage and retrieve. Different types of columns can store text, numbers, dates, or even choices from a predefined list.
Example: In a list of company contacts, columns might include “Name,” “Phone Number,” “Email Address,” and “Department.” Each column stores specific information about the contacts.
Content Type:
A content type is a reusable collection of settings and metadata that define a specific kind of content in SharePoint. It ensures consistency across similar items by applying the same structure, rules, and behaviors. Content types can include specific columns, workflows, and templates.
Example: A “Project Plan” content type might include columns for “Project Name,” “Start Date,” “End Date,” and “Project Manager.” Any document labeled as a “Project Plan” will follow this structure, making it easier to manage and find project plans across the organization.
Custom List:
A custom list is a user-created list in SharePoint designed to store and manage information in a structured format. Users can define the columns and settings according to their needs, making it a flexible tool for various tasks and data types.
Example: A custom list for tracking IT support tickets might include columns for “Ticket ID,” “Issue Description,” “Submitted By,” “Assigned To,” and “Status.” This allows the IT team to keep track of all support requests and their resolution status.
Document Library:
A document library in SharePoint is a specialized type of list designed to store and manage files. It supports version control, metadata tagging, and custom views, making it easy to collaborate on and organize documents.
Example: A document library for marketing materials might include folders for “Brochures,” “Presentations,” and “Logos.” Team members can upload new files, check out documents for editing, and track changes through version history.
External List:
An external list displays data from an external data source, such as a database or web service, using Business Connectivity Services (BCS). It allows users to view and interact with external data within SharePoint, as if it were part of the SharePoint environment.
Example: An external list showing customer orders from an ERP system. Employees can view order details, update statuses, and add comments directly within SharePoint, without needing to access the ERP system separately.
Farm:
A SharePoint farm is a collection of one or more SharePoint servers that work together to provide the SharePoint service. It includes various types of servers, such as web servers, application servers, and database servers, each handling different tasks to ensure the system runs smoothly and can handle large volumes of traffic.
Example: A large organization might have a SharePoint farm with multiple servers to support thousands of employees. The farm ensures high availability and scalability, so users experience fast and reliable access to SharePoint resources.
Field:
A field is a single piece of data in a SharePoint list or library, similar to a cell in a spreadsheet. Fields are defined by columns and store specific types of information, such as text, numbers, dates, or choices.
Example: In a project task list, fields might include the task name, due date, and status. Each field corresponds to a specific column, like “Task Name” or “Due Date,” and holds the relevant data for each task.
Hub Site:
A hub site in SharePoint is a special type of site that connects and organizes multiple related sites under a common structure. Hub sites provide unified navigation, search, and branding, helping users find content and collaborate across associated sites.
Example: A company might have a hub site for its marketing department, connecting sites for social media, content creation, and campaign management. The hub site provides a centralized navigation menu and search feature, making it easy for team members to find and access resources across all marketing sites.
InfoPath:
InfoPath is a Microsoft application used to design, distribute, fill, and submit electronic forms with structured data. InfoPath forms can be integrated into SharePoint to facilitate data entry and workflow automation, allowing users to collect and manage information efficiently.
Example: An employee expense report form created in InfoPath can be embedded in a SharePoint site. Employees fill out the form to submit their expenses, and the data is automatically routed for approval and processing.
List:
A list in SharePoint is a collection of data organized into rows and columns, similar to a table in a database. Lists can store various types of information, such as tasks, contacts, or events, and support features like sorting, filtering, and grouping to improve data management and retrieval.
Example: A list for tracking employee onboarding tasks might include columns for task description, assigned to, due date, and completion status. This helps HR manage and monitor the onboarding process for new hires.
Lookup Column:
A lookup column is a type of column in a SharePoint list that retrieves data from another list. It allows users to create relationships between lists, making it possible to reference data from one list in another.
Example: In a project task list, a lookup column might be used to select a project name from a separate project list. This creates a relationship between tasks and their associated projects, making it easier to manage and report on project activities.
Master Page:
A master page in SharePoint is a template that defines the overall layout and design of a site. It ensures a consistent look and feel across all pages by controlling elements such as the header, footer, and navigation menus. Custom master pages can be created to match an organization’s branding and design standards.
Example: A company might create a custom master page to include its logo, corporate colors, and navigation links in the header and footer. This ensures all SharePoint pages adhere to the company’s branding guidelines.
Metadata:
Metadata is data that provides information about other data, such as the author, date created, and keywords. In SharePoint, metadata helps organize, find, and manage documents by enabling advanced search, filtering, and sorting capabilities. Users can tag documents with relevant metadata to improve content discoverability and management.
Example: A document library for research papers might include metadata fields for “Author,” “Publication Date,” “Keywords,” and “Department.” This makes it easy to search for papers by specific criteria, such as all papers written by a particular author.
My Site:
My Site is a personal SharePoint site for individual users that provides features like personal storage, social networking, and a personalized newsfeed. It allows users to store and manage their own documents, share information with colleagues, and track activities and updates.
Example: John uses his My Site to store personal documents, such as project notes and drafts. He also follows his colleagues’ updates and shares links to interesting articles with his team through his newsfeed.
Navigation:
Navigation in SharePoint refers to the set of links and menus that allow users to move around a site. Effective navigation improves usability and access to content, helping users find information quickly and efficiently. SharePoint supports various navigation elements, including top navigation, quick launch, and breadcrumb trails.
Example: A SharePoint site for a sales team might have a top navigation bar with links to “Home,” “Leads,” “Opportunities,” “Reports,” and “Resources.” This helps team members easily find and access the information they need.
Office 365 Group:
An Office 365 Group is a shared workspace in Office 365 that includes a group mailbox, calendar, document library, OneNote notebook, and other collaboration tools. Office 365 Groups facilitate team collaboration by providing integrated tools for communication, file sharing, and task management.
Example: A project team creates an Office 365 Group for a new product launch. The group includes a shared mailbox for team emails, a calendar for scheduling meetings, a document library for storing project files, and a OneNote notebook for taking meeting notes.
OneDrive:
OneDrive is Microsoft’s cloud storage service that integrates with SharePoint for file storage and sharing. It allows users to store and protect files, share them with others, and access them from anywhere on all devices. OneDrive provides personal storage for users, while also enabling collaboration through shared libraries in SharePoint.
Example: Mary uses OneDrive to store her work documents. She shares a project folder with her team, allowing them to collaborate on documents and presentations. The shared folder is also accessible from the team’s SharePoint site.
Permissions:
Permissions in SharePoint are the set of rules that control what users can and cannot do on a site. Permissions can be set at the site, library, folder, or item level, allowing for granular control over access and actions. SharePoint supports role-based permissions, enabling administrators to assign predefined roles such as “Owner,” “Member,” and “Visitor” to users and groups.
Example: In a document library, an administrator grants “Read” permissions to visitors, “Contribute” permissions to members, and “Full Control” permissions to owners. This ensures that visitors can only view documents, members can add and edit documents, and owners can manage library settings.
Search:
Search functionality in SharePoint allows users to find content across sites and libraries. Search results can be customized with filters, refiners, and search scopes, helping users locate relevant information quickly. SharePoint search supports advanced features like content indexing, query suggestions, and result ranking to improve search accuracy and efficiency.
Example: A user types “annual report” into the SharePoint search bar and receives a list of all documents containing that term. They can filter results by date, author, or document type to find the specific report they need.
Site:
A site in SharePoint is a container that holds lists, libraries, pages, and other content. Sites can be created for different purposes, such as team collaboration, document management, or publishing. Sites provide a structured environment for organizing and managing content, supporting features like workflows, permissions, and branding.
Example: A department site for the HR team includes document libraries for employee policies, lists for tracking training sessions, and pages for sharing company news and announcements.
Site Collection:
A site collection in SharePoint is a group of sites that share common features, such as content types, templates, and permissions. A site collection includes a top-level site and any subsites below it, allowing for hierarchical organization and management of content. Site collections enable centralized administration and governance of related sites.
Example: A company might have a site collection for its intranet, with the main site serving as the home page and subsites for each department, such as HR, IT, and Finance. Each subsite inherits permissions and settings from the top-level site but can also have its own unique content and structure.
Site Template:
A site template is a pre-defined configuration of a SharePoint site that includes specific lists, libraries, and settings. Site templates can be used to create new sites with a consistent structure, saving time and ensuring uniformity. SharePoint includes built-in site templates for common scenarios, such as team sites, project sites, and publishing sites.
Example: A project site template might include a task list, document library, and calendar, providing a standardized setup for managing new projects. When a new project starts, the team can quickly create a site using this template.
SPFx (SharePoint Framework):
The SharePoint Framework (SPFx) is a page and web part model that provides full support for client-side development, integration with SharePoint data, and support for open-source tools. SPFx enables developers to create responsive and dynamic web parts and extensions using modern web technologies. It enhances the customization and extensibility of SharePoint, allowing for rich and interactive user experiences.
Example: A developer creates a custom SPFx web part that displays a real-time dashboard of sales data, integrating with external APIs and SharePoint lists. The web part can be added to any SharePoint page, providing interactive and visually appealing data insights.
Team Site:
A team site in SharePoint is designed for team collaboration, providing tools for document sharing, task management, and communication. Team sites include features like document libraries, calendars, and discussion boards, enabling teams to work together effectively. Team sites can be customized to meet specific team needs and integrated with other Office 365 services.
Example: A sales team uses a team site to store client proposals, track sales leads, and schedule meetings. The site includes a document library for shared files, a calendar for team events, and a task list for tracking sales activities.
Term Store:
The Term Store is a feature in SharePoint that allows you to manage metadata and taxonomies centrally. Terms can be used to tag and categorize content across sites, improving consistency and searchability. The Term Store supports hierarchical term sets, synonyms, and multi-language support, facilitating effective metadata management.
Example: A company uses the Term Store to manage a taxonomy of product categories. Documents in the product library are tagged with terms like “Electronics,” “Home Appliances,” and “Furniture,” making it easy to organize and search for documents by category.
Version Control:
Version control is a system in SharePoint that records changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later. Version control helps track document history and manage edits by multiple users, providing a clear audit trail. SharePoint supports major and minor versioning, allowing for detailed tracking of changes and approvals.
Example: A marketing team uses version control for their campaign plans. Each time a plan is edited, a new version is saved. If the team needs to revert to a previous version or see who made specific changes, they can access the version history.
Web Part:
A web part is a modular unit of information that can be added to a SharePoint page. Web parts can display data, provide interactivity, and integrate with other systems. Examples of web parts include document libraries, lists, image galleries, and embedded videos. Web parts enable users to create dynamic and customizable pages, enhancing the functionality and user experience of SharePoint sites.
Example: A company homepage might include a news web part to display recent announcements, a calendar web part to show upcoming events, and a document library web part to provide quick access to important documents.
Workflow:
A workflow in SharePoint is a sequence of automated steps that perform specific actions, such as approving a document or sending an email. Workflows help streamline business processes and ensure consistency by automating repetitive tasks. SharePoint includes built-in workflows for common scenarios, such as document approval, feedback collection, and task management. Custom workflows can also be created using tools like Microsoft Power Automate.
Example: An expense report approval workflow automatically routes submitted reports to the appropriate managers for approval. Once approved, the workflow sends the report to the finance department for processing and notifies the employee of the approval status.
Zone:
A zone is a section of a SharePoint page layout that can hold web parts. Zones help organize and arrange content on a page, allowing for flexible and responsive design. Zones enable users to customize the layout and presentation of information, enhancing the visual appeal and usability of SharePoint pages.
Example: A team site homepage might be divided into zones for announcements, quick links, and a document library. Each zone contains web parts that display relevant content, making it easy for team members to find and access information.